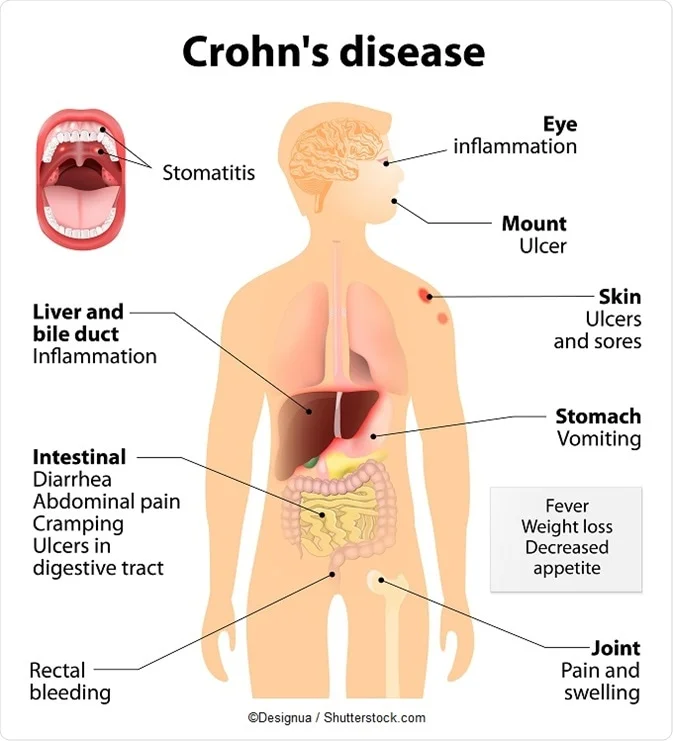
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-term inflammation in the digestive tract. The cause of Crohn’s disease is still unknown, but it’s thought to be an autoimmune disorder. Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive tract, causing a wide variety of symptoms.

It causes a wide range of symptoms, which can affect the quality of life, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. There is no cure for Crohn’s, but symptoms can be managed with diet and lifestyle changes, medication, and surgery.
Its area concentration is centered in “inflammation in the lining of the digestive tract”, which causes a wide variety of symptoms. The exact causes of Crohn’s disease are still unclear, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Current treatments for Crohn’s disease include medications and surgeries to manage the symptoms.
CAUSES OF CROHN’S DISEASE:
This also makes it difficult to diagnose. Researchers have identified several known risk factors for developing Crohn’s disease, including poverty, certain infections, and certain medical conditions.
There are also a number of unknown risk factors that increase your chance of developing Crohn’s disease, including Sometime between birth and age 20, people are born with bacteria in their intestines that may or may not become inflamed.
This is called the gut microbiome. It often begins with stomach cramps and diarrhea, but can quickly lead to more serious complications, including obstruction of the bowel, surgery, and death. Most people with Crohn’s disease experience diarrhea and abdominal cramping.
There are several forms of Crohn’s disease, and symptoms may differ between forms. There are currently no known treatments that can cure Crohn’s disease, but treatments can help manage the disease and its symptoms.
WHAT FOOD TRIGGERS CROHN’S DISEASE?
One of the biggest risk factors for developing Crohn’s disease is the food you eat. Certain foods can trigger inflammation in your intestines, which may trigger symptoms of Crohn’s disease. The two most common food triggers for Crohn’s disease are gluten and dairy. Research has shown that a strict gluten-free diet can reduce the symptoms of Crohn’s disease in some people.
The gut microbiome is the collection of bacteria, viruses, and other microbes that live in the digestive tract. The types of bacteria in the gut microbiome can affect the health of the digestive tract in many ways, but one of the biggest effects on the health of the digestive tract is the presence or absence of certain types of bacteria. The composition of the gut microbiome changes over time as a person ages. This can affect the types of bacteria that are present, and this in turn can affect the health of the digestive tract.
WHAT MAKES CROHN’S DISEASE WORSE?
One of the biggest risk factors for developing Crohn’s disease is the food you eat. Certain foods can trigger inflammation in your intestines, which may trigger symptoms of Crohn’s disease. The two most common food triggers for Crohn’s disease are gluten and dairy. Research has shown that a strict gluten-free diet can reduce the symptoms of Crohn’s disease in some people.
It’s best to talk to your doctor about whether or not it’s safe for you to follow a gluten-free diet. Also, limiting or eliminating dairy may also help reduce your symptoms. It’s generally safe to follow a dairy-free diet if you’re already following a gluten-free diet.
However, the best diet for managing Crohn’s disease depends on you and your symptoms. There isn’t a “typical” diet that will work for everyone with Crohn’s disease. It’s important to discuss your diet with a nutritionist if you have questions about managing Crohn’s disease symptoms. There is no “cure” for Crohn’s disease.
Avoiding potential food triggers is the best way to manage your symptoms. A diet that’s high in fiber, vegetables, and fruit, and low in sugar, starches, and protein may also help manage your symptoms. But, not everyone is able to follow a gluten-free diet.
There are also many other dietary restrictions that can help reduce the symptoms of Crohn’s disease. Some doctors recommend a diet that eliminates all foods that may trigger symptoms, such as gluten and dairy. This is called a Paleo diet, or the caveman diet.
Read also:
- Kim Kardashian Shares Heartfelt Heavenly Birthday Message to Dad Rob Kardashian
- Next time I won’t wear anything – Kelly Khumalo fires back at critics after singing gospel music in skimpy outfit (videos)
- Zinoleesky And Mohbad Arrested By NDLEA
- Run From Toxic Relationships – Lady Warns After Being Attacked By Her Boyfriend On Her Birthday (video)
- ”Soft and Single”- Reality TV star, Vee, confirms her relationship with Neo Akpofure is over
- “Husbands Must Be Older Than Their Wives, Not Vice Versa” – Reno Omokri
- Reactions As Bobrisky’s Name Gets Missing in Unilag
- Carabao Cup Final: Berbatov Predicts Scoreline Between Chelsea and Liverpool
WHAT FOOD REDUCE INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION?
The main way to reduce intestinal inflammation is to eat a healthy diet that’s low in inflammation-causing foods, such as refined carbohydrates, added sugar, and processed foods. This helps keep your digestive system healthy and reduces your risk of developing Crohn’s disease.
You can also try to reduce your overall stress levels since stress can also increase your risk of developing Crohn’s disease. And finally, you can also try to increase your level of physical activity. Research has shown that following a diet that’s low in fat and high in fiber can help reduce inflammation in the intestines, which may help reduce the symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
One study looked at the diets of people with Crohn’s disease and found that following a low-fat diet and eating foods that are high in fiber may reduce the symptoms of Crohn’s disease. In another study, people with Crohn’s disease followed a low-fat diet that was also high in fiber. After four months, their Crohn’s disease symptoms were reduced.
HOW QUICKLY DOES CROHN’S DISEASE DEVELOP?
The speed at which Crohn’s disease develops also depends on your age, immune system, and other underlying health conditions. In most cases, people with Crohn’s disease don’t notice any symptoms until they’re much sicker than their friends with Crohn’s disease.
But some people with Crohn’s disease first experience symptoms such as severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss at an earlier stage of the disease. The main risk factor for developing Crohn’s disease is the location where the disease begins to develop in your body.
Crohn’s disease most often begins in your small intestine, although it can begin in your colon or other parts of your digestive system. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease typically develop slowly over time.
CONCLUSION; These symptoms may disappear over time, or they may progress and become more severe. In some cases, Crohn’s disease may be diagnosed by testing your blood. But this isn’t always possible, or reliable. So in most cases, it’s important to see a doctor, who can diagnose Crohn’s disease based on your symptoms and medical history.
If you think you or someone you know may have Crohn’s disease, it’s important to let your doctor know as soon as possible.
This can help improve your chances of receiving the treatment that’s right for you. Once you have Crohn’s disease, it can remain in your body for the rest of your life. But you can reduce your risk of developing complications if you follow a healthy diet, get plenty of physical activity, and manage your symptoms as early as possible.
And if you are diagnosed with Crohn’s disease, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes or medications to help manage your symptoms and slow the disease process.


![Man Receives Pig Kidney Transplant and Leaves Hospital in good condition 4 Rick Slayman, the first man to get a kidney transplant from a pig and his doctors [cnn]](https://loadedvibesng.com/sitsyghu/2024/04/Man-who-got-new-kidney-from-a-pig-released-from-hospital.avif)